Decision support in acute stroke
Title: AI-based decision support in acute stroke
Research Area: Life Science and Medicine
Aims
ScaDS.AI Dresden/Leipzig and the Image and Signal Processing Group of the Leipzig University collaborate closely with the Neuroimaging Lab at the Leipzig University Medical Center to advance stroke research. Together, we focus on leveraging cutting-edge AI methods to support better-informed and individualized decision-making in stroke care, thereby advancing translational neuroscience. ScaDS.AI Dresden/Leipzig brings AI expertise to the project, while the Neuroimaging Lab contributes medical expertise and maintains a comprehensive database of clinical and imaging data from stroke patients treated in their stroke unit.
Problem
Endovascular thrombectomy – a procedure to remove blood clots from large arteries in the brain – has significantly improved outcomes for stroke patients. However, determining who will benefit from this treatment is crucial, as individual responses can vary widely. Current patient selection methods rely on perfusion CT scans to map blood flow in the brain, but these may not fully capture the dynamic nature of a stroke and don’t assess the benefits of thrombectomy on an individual basis.
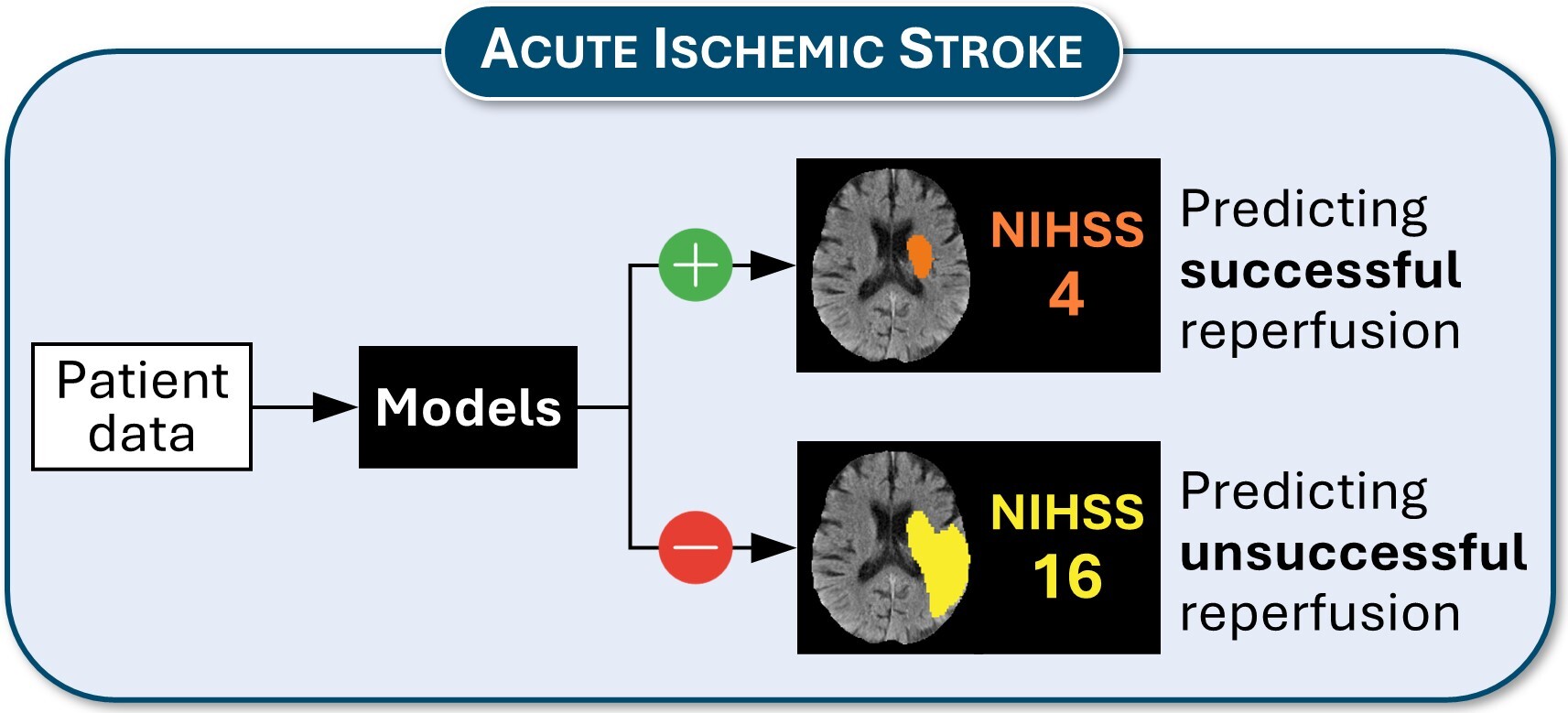
Approach
One of our projects focuses on developing a deep learning method to predict how individual stroke patients might respond to thrombectomy. Our models provide forecasts for both brain tissue health and clinical recovery under two scenarios: one where blood flow is successfully restored and another where it isn’t. By comparing these predictions, we can estimate the potential benefits of the procedure for each patient.
Technology
For this, we built an advanced 3D neural network that analyzes CT scans and patient data. This network incorporates personal factors like age and medical history and uses attention mechanisms to focus on critical details. We trained our models using data from 405 stroke patients who underwent thrombectomy, including their imaging, clinical characteristics, and recovery results.
Outlook
By offering personalized predictions of treatment outcomes, our approach provides a new tool that reflects the evolving nature of a stroke. We believe this method has significant potential to improve patient selection for endovascular thrombectomy, ensuring that those who will benefit the most receive the treatment.
More information
As part of the Digital Mobile Classroom (DigiMoK) initiative, which promotes education around artificial intelligence, coding, and robotics in schools, an interview about our stroke research has been conducted in collaboration with Helliwood media & education.
Publications
- von Braun M-S, Stoll K, Peter L, et al. Prediction of Tissue and Clinical Thrombectomy Outcome in Acute Ischaemic Stroke Using Deep Learning. Brain. 2025;awaf013. doi:10.1093/brain/awaf013
- von Braun M-S, Stoll K, Peter L, et al. Overcoming thresholds – Utilizing convolutional neural networks for predicting individual thrombectomy response in acute ischemic stroke. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2024;159:e8. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2023.12.027
- Stoll K, von Braun M-S, Kürsten D, et al. Prediction of functional therapeutic response to thrombectomy in acute stroke using neural networks. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2024;159:e5. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2023.12.021
- Welle F, Stoll K, Gillmann C, et al. Tissue Outcome Prediction in Patients with Proximal Vessel Occlusion and Mechanical Thrombectomy Using Logistic Models. Translational Stroke Research. 2023. doi:10.1007/s12975-023-01160-6
- Gillmann C, Saur D, Scheuermann G. How to deal with Uncertainty in Machine Learning for Medical Imaging? In: 2021 IEEE Workshop on TRust and EXpertise in Visual Analytics (TREX). IEEE; 2021:52-58. doi:10.1109/TREX53765.2021.00014
- Gillmann C, Peter L, Schmidt C, Saur D, Scheuermann G. Visualizing Multimodal Deep Learning for Lesion Prediction. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications. 2021;41(5):90-98. doi:10.1109/MCG.2021.3099881
- Gillmann C, Saur D, Wischgoll T, Scheuermann G. Uncertainty-aware Visualization in Medical Imaging – A Survey. Computer Graphics Forum. 2021;40(3):665-689. doi:10.1111/cgf.14333
- Gillmann C, Saur D, Wischgoll T, Hoffman K, Hagen H, Maciejewski R, Scheuermann G. (2020). Uncertainty-aware Brain Lesion Visualization. Eurographics Workshop on Visual Computing for Biology and Medicine (EG VCBM), 97-101. https://corescholar.libraries.wright.edu/cse/591
Team
Lead

Prof. Dr. Gerik Scheuermann
Leipzig University
Chair of Image and Signal Processing
- Prof. Dorothee Saur (University of Leipzig Medical Center)
Team Members

Marie-Sophie von Braun
Leipzig University

Dr. Christofer Meinecke
Leipzig University
- Dr. Kristin Starke (University of Leipzig Medical Center)


