LLM4Edu: Learning Large Language Models on Graphs for Education
Title: LLM4Edu: Learning Large Language Models on Graphs for Education
Project duration: 01.01.2025 – 31.05.2026
Research Area: Understanding Language, Large Language Models, Natural Language Processing


Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable In-Context Learning (ICL) capabilities with no or limited training data, such as understanding human language and answering general questions. However, fine-tuning these models for specific tasks is essential for their adaptability, particularly in the educational sector, where they promise to revolutionize learning environments and have a profound societal impact. In collaboration with Macmillan Learning, the project LLM4Edu aims to develop next-generation AI tools specifically tailored for educational applications. By employing graph-based methods, we will extract meaningful datasets from unstructured user data, facilitating the development of parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods that are particularly suited to educational contexts.
Traditional fine-tuning methods often impose significant computational demands. As model sizes increase, realistically fine-tuning all parameters becomes increasingly challenging. Various Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods for LLMs, such as Adapter, Prefix-tuning, Prompt-tuning, and LoRA, have been introduced. While these methods reduce training costs to some extent, they often lack a thorough understanding of their underlying mechanisms, resulting in a lack of interpretable PEFT approaches.
In this project, we propose a novel benchmark by creating a graph-based dataset specifically tailored for personalized educational usage. Furthermore, we develop an interpretable PEFT method that leverages Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). This method aims not only to reduce the training budget but also to provide an intuitive understanding of the operational mechanisms involved. Moreover, we will analyze unstructured data from Macmillan Learning to extract meaningful information, constructing a structured dataset that applies graph-based methods. This dataset will explore the potential applications of data within educational contexts, enabling more personalized, responsive, and effective learning experiences.
Aims
The primary aim of the project is to develop an educational dataset and introduce a graph-based PEFT method designed to optimize the fine-tuning process for LLMs. This approach leverages insights from both the information flow perspective inherent to ICL and the information aggregation processes of GNNs. Our proposed method seeks to minimize training resource requirements while enhancing the interpretability of the fine-tuning process. The specific goals of the project are outlined as follows:
1. Develop a benchmark dataset tailored for educational use, designed to support the specific demands and nuances of educational environments. This dataset will serve as a foundational tool for testing and improving AI applications in educational settings.
2. Create a novel PEFT method that not only reduces the training resources required by LLMs but also highlights the most significant parameters within these models. This enhancement will increase transparency and interpretability, crucial for educational stakeholders to trust and effectively utilize AI tools.
3. Bridge the gap between LLMs and GNNs by using GNNs to encode complex relationships in LLMs, specifically tailored to personalized learning objectives. This integration aims to utilize the strengths of both technologies to foster a more nuanced understanding and application of AI in personalized education.
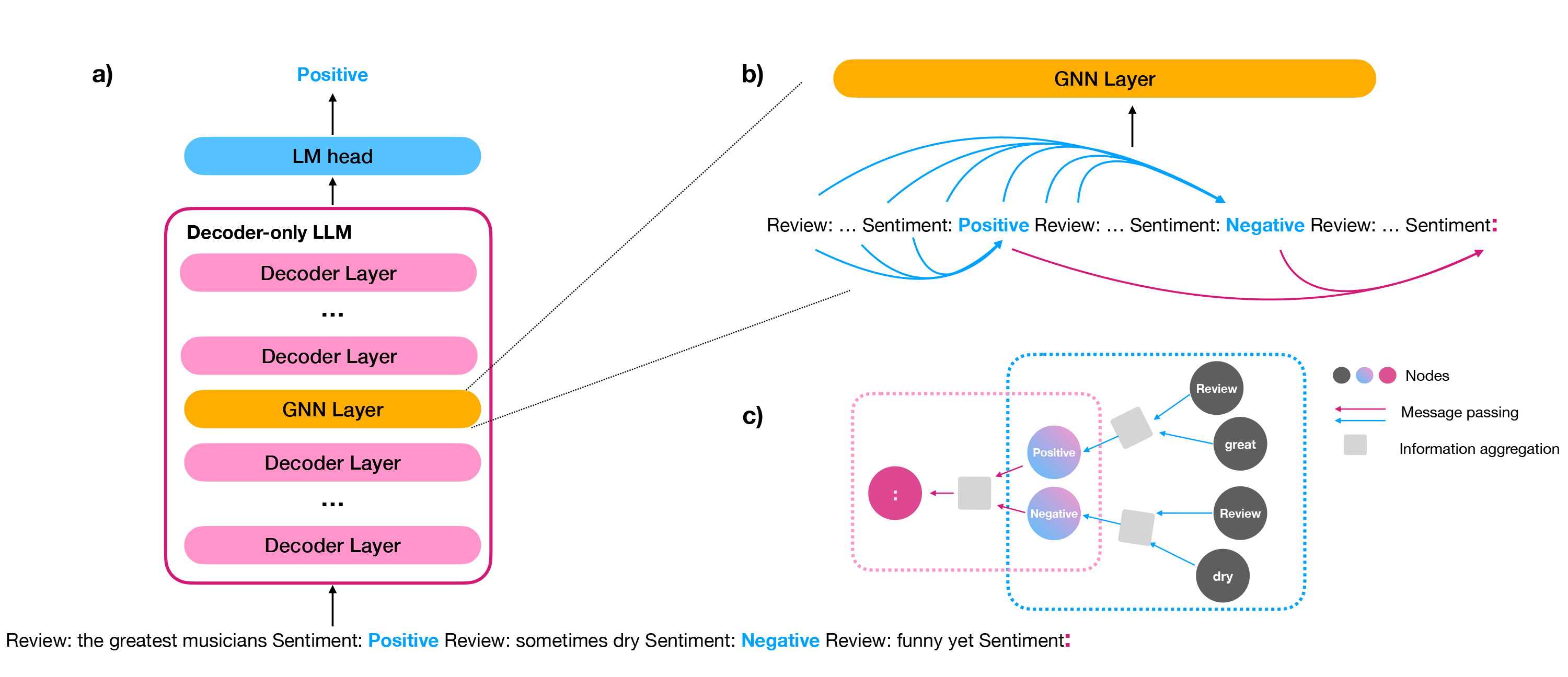
Problem
Throughout LLM4Edu, we will explore several pivotal research questions aimed at enhancing the application of AI in educational settings:
- Dataset Creation: How can we effectively design and create an education-specific benchmark dataset from the unstructured data provided by Macmillan Learning? What methods will ensure that this dataset encapsulates the complexities and variances of educational data?
- Model Optimization: Which components in LLMs are most significant for educational applications? Can we achieve desired learning outcomes by selectively fine-tuning these critical parameters rather than the entire model?
- Educational Enhancement: How can tailored LLMs enhance the digital learning and teaching experiences for students and educators? What specific attributes of LLMs can be leveraged to support personalized educational journeys?
Technology
We plan to implement LLM4Edu by combining the most sophisticated research in parameter-efficient fine-tuning with novel methods from the graph perspective. To highlight the most significant components in LLMs, we will draw inspiration from recent findings in in-context learning and saliency score, hardwiring the connections of the most important tokens in the input text. Unlike previous methods, we will explore different connections between tokens and elucidate the working mechanism of the PEFT method. By integrating GNN to LLMs, we will keep the parameters of LLMs frozen and only update GNN’s parameters to reduce the training budget.
Transfer learning provides a solution for transferring knowledge among NLP tasks, but transferring knowledge among models is understudied. A recent method proposed a technique of combining LLMs with a linear layer. Building on this method, we plan to implement a novel approach using GNNs to transfer knowledge from a small model to a large model. We will also explore different GNN architectures such as GCN, GAT, GraphSAGE, etc.
Team
Lead

Shuzhou Yuan
TUD Dresden University of Technology
Chair of Scalable Software Architectures for Data Analytics
Team Members

Prof. Dr.-Ing. Michael Färber
TUD Dresden University of Technology
Chair of Scalable Software Architectures for Data Analytics
Partners


